Loci in the Argand Diagram
Introduction
⇒ Complex numbers can be used to represent a locus of points on an Argand diagram
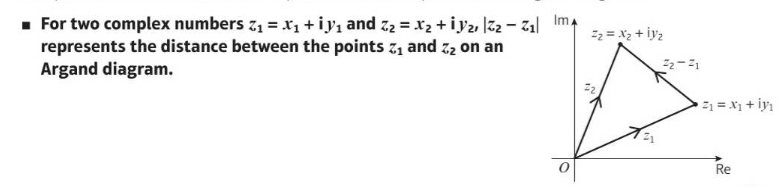
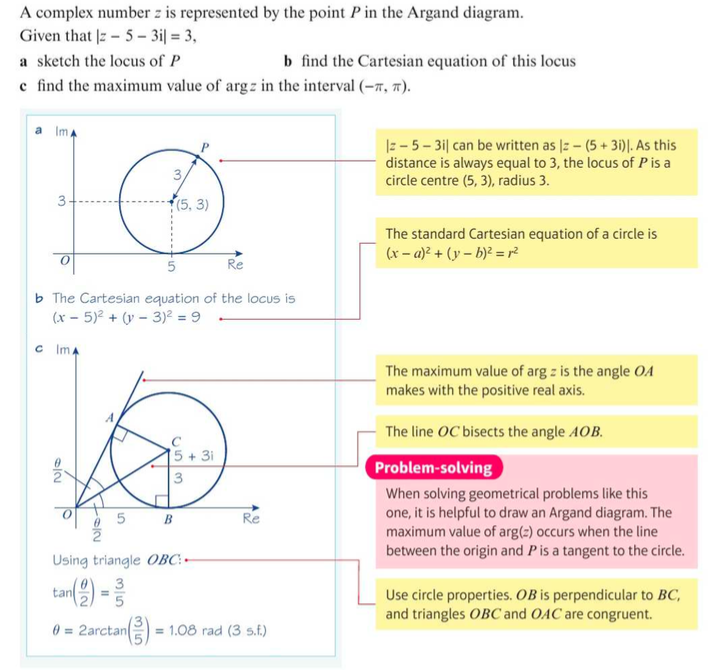
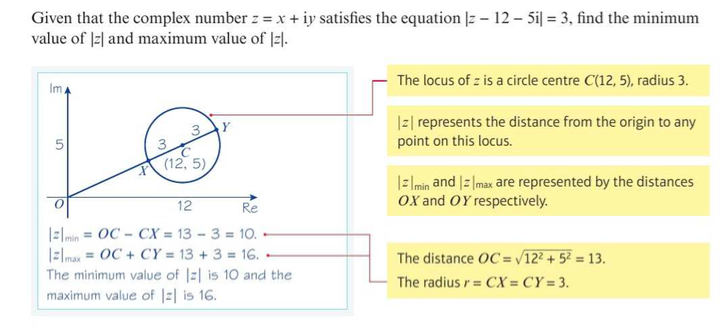
⇒ Using the above result, you can replace z2 with the general point z. The locus of points described by |z - z1| = r is a circle with centre (x1, y1) and radius r


⇒ You can derive a Cartesian form of the equation of a circle from this form by squaring both sides:

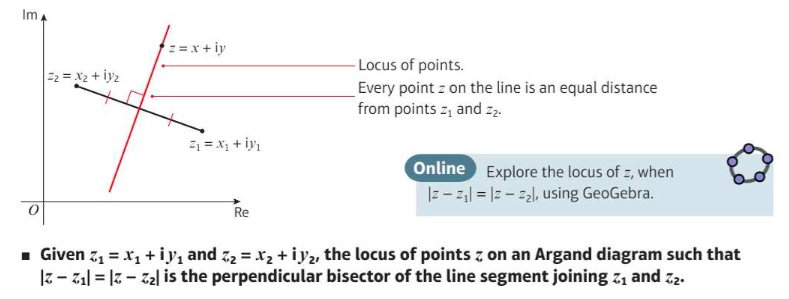
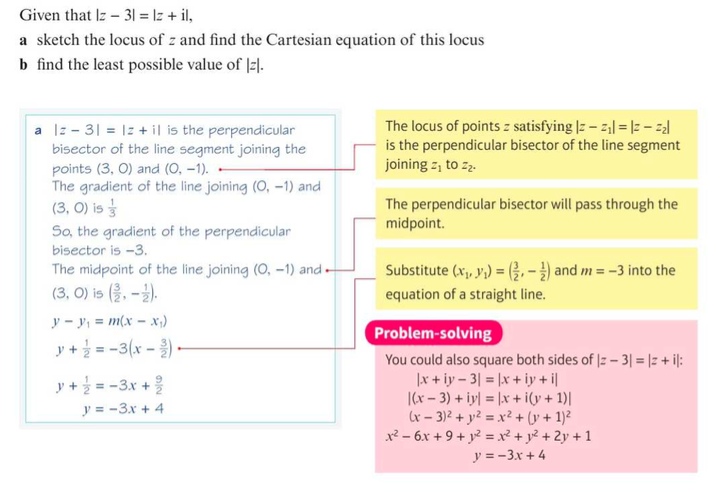
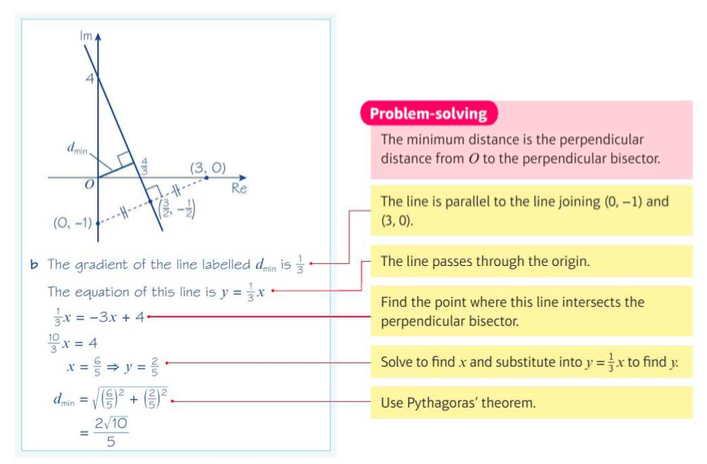
⇒ The locus of points that are an equal distance from two different points z1 and z2 is the perpendicular bisector of the line segment joining the two points
Examples
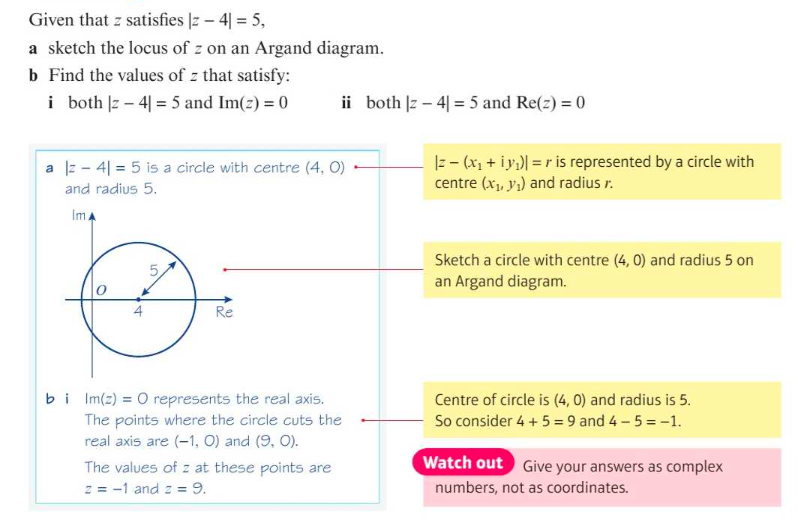
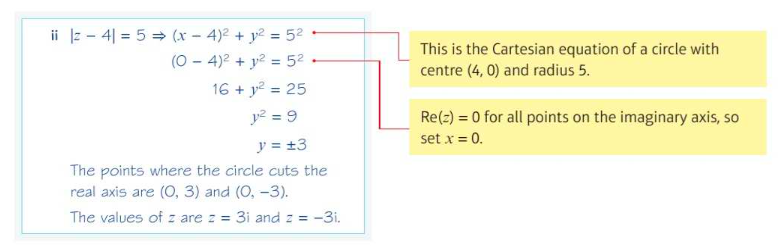
Geometric Property
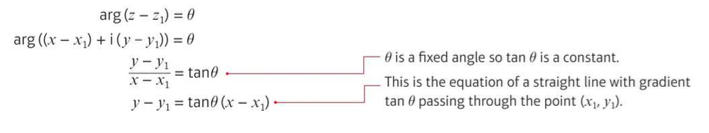
⇒ Locus questions can also make use of the geometric property of the argument

⇒ You can find the Cartesian equation of the half-line corresponding to arg(z - z1) = θ by considering how the argument is calculated:
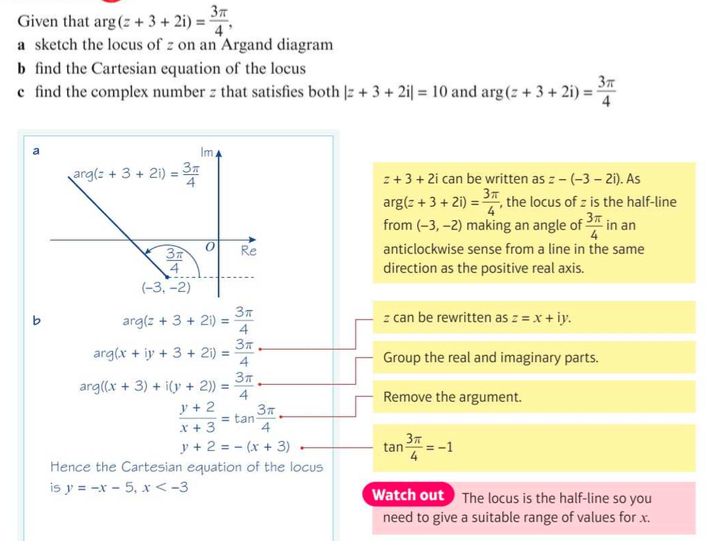
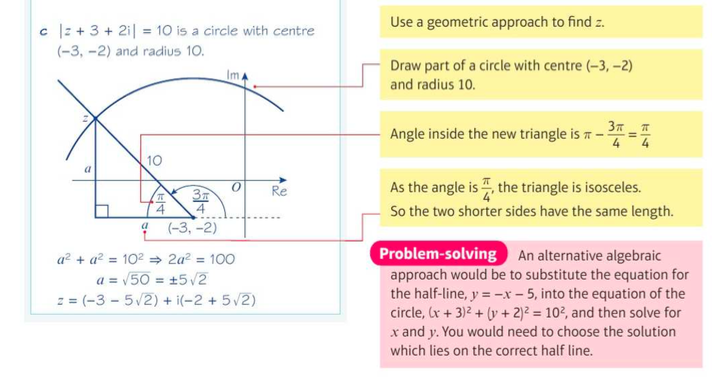
Examples
Extra
⇒ Also see our notes on: