Newton's Third Law of Motion
Introduction
⇒ This law states that every force has a paired equal and opposite force
⇒ It is important to remember that the forces must act on two different bodies and the forces must be the same type of force
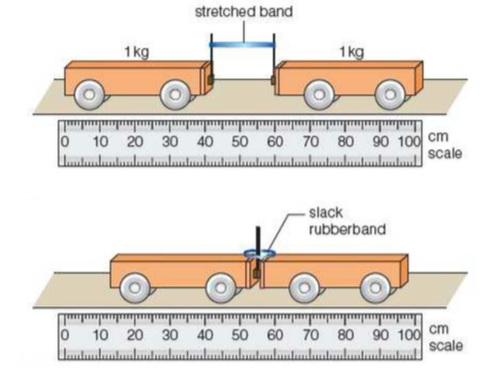
⇒ This law can be demonstrated using two pulleys which are connected by a stretched rubber band, as seen above
⇒ When the trolleys are released, they travel the same distance and meet in the middle
- What you are seeing is trolley A exerting a force on trolley B, and trolley B exerts a force of the same size, in the opposite direction, on trolley A
Paired Forces
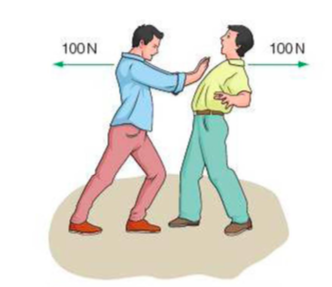
⇒ If I push you with a force of 100N, you push me back with a force of 100N
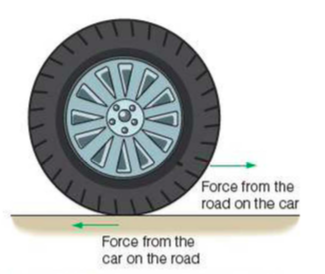
⇒ When the wheel of a car turns it pushes the road backwards, and the road pushes the wheel forwards with an equal and opposite force
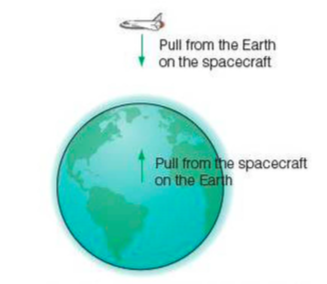
⇒ A spacecraft orbiting the Earth is pulled downwards by Earth's gravity. The spacecraft exerts an equl an opposite gravitational pull on Earth - so if the spacecraft moves towards Earth, the Earth moves too, but because Earth is so big the movement is tiny
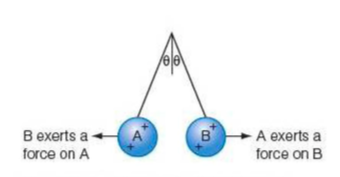
⇒ Here we see two positively charged balloons, which are repulsive. These forces are of the same size, so each balloon (if of the same mass) is lifted through the same angle
Newton's third law pairs
⇒ Newton's third law pairs always have these properties:
- They act on two separate bodies
- They are of the same type, for example two electrostatic forces or two contact forces
- They are of the same magnitude
- They act along the same line
- They act in opposite directions
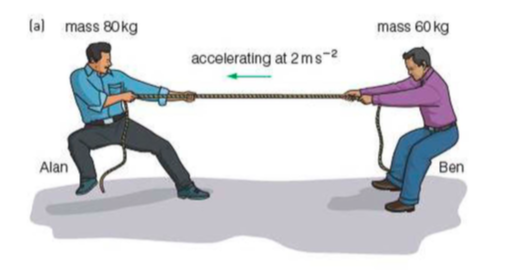
A tug of war
⇒ Alan and Ben are playing a game of tug of war
⇒ Alan is beginning to win - Alan, Ben and the rope are accelerating to the left at 2ms-2
⇒ By drawing a free body diagram for Alan (mass 80kg), the rope (mass 2kg) and Ben (mass 60kg), we can analyse the forces acting on each person
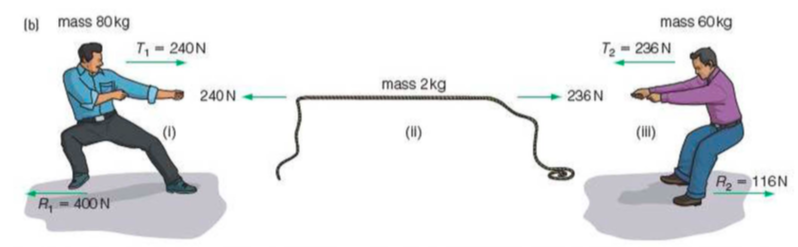
⇒ For each body the resultant force caused an acceleration of 2 ms-2. These calculations use Newton's second law.
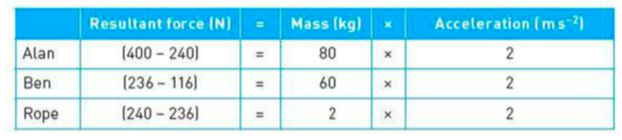
Newton's third law pairs
⇒ The Earth pushes Alan with 400N to the left. Alan pushes the Earth with 400N to the right
⇒ The Earth pushes Ben with 116N to the right. Ben pushes the Earth with 116N to the left
⇒ The rope's tension pulls Alan to the right with 240N. Alan pulls the rope to the left with 240N
⇒ The rope's tension pulls Ben to the left with 236N. Ben pulls the rope to the right with 236N
Extra
⇒ Also see our notes on: