Devolution of Northern Ireland
Introduction
Devolution
⇒ Devolution is not a term of art in constitutional law
⇒ It signifies the shift of power from the centralised institutions to their regional or national counterparts
⇒ Devolution is a relatively recent process in the UK → until recently Westminster was the locus of legislative power, but since 1998 (at the least) this has been changing through devolution
Unitary v Federal States
⇒ A unitary state is a sovereign state governed as one single unit in which the central government is supreme and any administrative divisions (subnational units) exercise only powers that the central government chooses to delegate. Example include:
- France, Japan, and Italy. The UK has traditionally been described as a unitary state, but it is difficult to describe the UK as a purely unitary state today (it appears to be increasingly federal)
⇒ A federal state is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing states or regions under a central (federal) government. Examples include:
- Germany, Australia and the USA
⇒ Through devolution a unitary constitution can become a federal constitution; so devolution is a process where a former unitary state becomes a federal state
Devolution and Independence
⇒ Devolution provides for a limited and carefully circumscribed degree of self-governance. It is not the same as independence because:
- In the UK context, the Westminster Parliament retains the legal right to legislate on ‘reserved’ matters (reserved matters are matters which are not devolved)
- The grant of devolution is something that the Westminster Parliament can revoke
⇒ So Parliament ultimately retains its sovereignty
- However, devolution may put a chain of events into place where the ‘devolved’ nation seeks to exceed its mandate
- This was always the fear of political conservatives whenever devolution was presented as an idea
- In other words, although devolution does not provide for independence it may lead to it!
Devolution: Taxonomy
⇒ The narrow meaning of devolution (administrative devolution)
- Under the narrow meaning, devolution is a de-concentration of functions within the governmental hierarchy
⇒ The broad meaning of devolution (legislative and/or executive devolution) → this is what we mean when we talk about devolution
- Under the broad meaning there is a transfer of central powers to regional bodies
- Legislative devolution involves the transfer of power to determine policy
- Executive devolution involves the transfer of power to subordinate policy making and administration
The Art of Getting a First in Law - ONLY £4.99
FOOL-PROOF methods of obtaining top grades
SECRETS your professors won't tell you and your peers don't know
INSIDER TIPS and tricks so you can spend less time studying and land the perfect job
We work really hard to provide you with incredible law notes for free...
The proceeds of this eBook helps us to run the site and keep the service FREE!

The UK and Ireland
Ireland: context
⇒ In UK constitutional law, Ireland was part of the United Kingdom until the early-twentieth century (the UK did not formally recognise the Republic of Ireland until 1949).
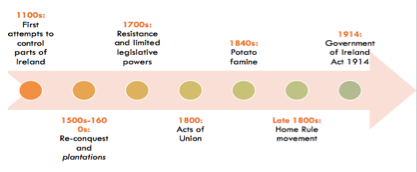
⇒ The Acts of Union allowed Irish MPs to sit in Westminster
⇒ Since 1800s the Home Rule movement began - the idea we now call devolution (Ireland had a long desire to be self-governed)
- There was a fear that there would be a loss of religious and economic freedoms in Ireland if they were self governed
- The Conservative House of Lords was very much against Home Rule as they thought it would lead to the end of the UK, however that was not the purpose of the Home Rule movement
⇒ The Government of Ireland Act 1914 was an Act of Parliament to give Home Rule to Ireland. But, the onset of World War I led to the postponement of the provisions of the 1914 Act.
⇒ The Irish War of Independence finally ousted the British—but at a great cost
- The legal settlement (Anglo-Irish Treaty, signed in 1921) provided for Britain’s acceptance of an independent Irish state subject to the right of Ulster (Northern Ireland) to remain part of the UK if it so chooses
- Almost immediately, Ulster elected to remain part of the UK.
Northern Ireland
Devolution 1921-1972
⇒ The newly created identity of Northern Ireland (six counties to the north of Ireland) enjoyed a degree of self-government until its powers were suspended in 1972
⇒ Legislative power was transferred in large part from Westminster to the Parliament at Stormont in Belfast → the Government of Ireland Act 1920 stated which powers would be retained by parliament and which powers would be transferred
⇒ Northern Ireland was governed directly by Westminster again from 1972
A Peace Process (after 1997)
⇒ Motivated by the prospect of of securing peace on both islands, Tony Blair and Bertie Ahern (Irish Taoiseach) led efforts to achieve devolution through legal change
⇒ The (multi-party) deal was enshrined in the Good Friday Agreement 1998 and the two governments concluded an (international) Anglo-Irish Agreement 1999
⇒ Both the Irish Constitution and UK law would be amended to appease both ‘sides’ of the unionist/republican divide
⇒ Devolution in Northern Ireland was to be about peace and power sharing
Legal Changes in the UK
⇒ “Northern Ireland in its entirety remains part of the United Kingdom“
⇒ “But if the wish expressed by a majority in such a poll is that Northern Ireland should cease to be part of the United Kingdom and form part of a united Ireland, the Secretary of State shall lay before Parliament such proposals to give effect to that wish” (Northern Ireland Act 1998 s.1)
Northern Ireland Act 1998
⇒ The Northern Ireland Act 1998 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which established a devolved legislature for Northern Ireland, the Northern Ireland Assembly, after decades of direct rule from Westminster
- The Northern Ireland Assembly consists of 108 members who are elected for a term of 4 years and have limited transferred powers/competences
⇒The legislative competences of Northern Ireland (what they can legislate on):
- Section 6(1) of the Northern Ireland Act says a “provision of an Act is not law if it is outside the legislative competence of the Assembly.”
- Northern Ireland can legislate on Transferred matters
- Northern Ireland cannot legislate on Excepted matters (Schedule 2)
- Northern Ireland cannot legislate on Reserved matters (Schedule 3), unless further conditions are met:
- There is cross-community support i.e. where there is a majority of votes from both the unionists and the nationalists
- There is an order in council i.e. legislation made by the sovereign on the advice of the Privy Council
⇒ Transferred competences include education, health, arts & culture, and agriculture & rural development
⇒ Excepted matters include international relations, taxation, elections, and the army & defence
⇒ Reserved matters include criminal justice, financial services, and intellectual property
Sovereignty
⇒ Sovereignty is retained by the Westminster Parliament
⇒ This is confirmed in law by section 5(6) Northern Ireland Act 1998: "This section does not affect the power of the Parliament of the United Kingdom to make laws for Northern Ireland."
⇒ This is also confirmed in practice: in 2000 the Executive was suspended for around 3 months
Law Application Masterclass - ONLY £9.99
Learn how to effortlessly land vacation schemes, training contracts, and pupillages by making your law applications awesome. This eBook is constructed by lawyers and recruiters from the world's leading law firms and barristers' chambers.
✅ 60+ page eBook
✅ Research Methods, Success Secrets, Tips, Tricks, and more!
✅ Help keep Digestible Notes FREE