Analogue and Digital Signals
Sending Information
⇒ There are two different ways of sending information: either by analogue or by digital signals
The Signals
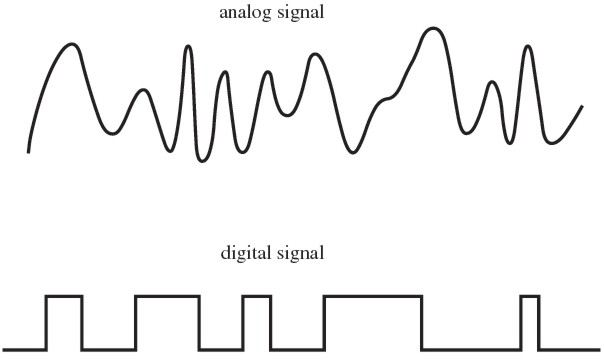
⇒ The analogue signal varies continuously in both amplitude and frequency and the signal can take one of many different values
⇒ The digital signal can only take two values, either a 1 or a 0 (which is sometimes called 'on' or 'off')
- Digital signals are sent as a series of pulses of either 1s or 0s
⇒ Examples of analogue devices include dimmer switches,thermometers, speedometer and old-fashioned watches
Amplifying signals
⇒ Both digital and analogue signals weaken as they travel, so they may need to be amplifiedalong their route
⇒ They also pick up interferences or noise from electrical disturbances or other signals
Which signal is better?
⇒ Digital is a much better way of sending information over long distances
- With digital signals, noise is far less of a problem because a noisy digital signal is still quite clear what is meant to be shown (in other words, even when the digital signal is slightly distorted, it is still easy to see whether its value is a 1 or a 0
⇒ A noisy analogue signal is much more difficult to tell what the original signal was. Additionally, when you amplify a noisy analogue signal, you amplify the noise too.
⇒ The other benefit of digital signals is that they are processed far better by laptops as they are digital too