Escape Velocity
Summary
⇒ The Earth has its atmosphere because the molecules of gas, moving around the planet, do not have enough kinetic energy to escape the Earth's gravitational pull
⇒ So, how fast does something have to move to escape Earth's surface?
⇒ When a fast moving object leaves the suface of a planet, we can write: decrease in kinetic energy = increase in gravitational potential energy
⇒ This assumes that the object is not affected by an atmosphere, and is in free fall - this is not a spacecraft with a rocket
⇒ The equation above can be written as:
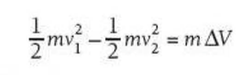
⇒ If the object is to just escape the pull of the planet, its speed, V2, will just reach zero at an infinite distance from the planet
⇒ This leads to the idea of escape velocity, which is the minimum velocity that an object must have at the surface of a planet in order to escape the pull of gravity of the planet using its own kinetic energy
Formulas
⇒ The gravitational potential at the surface of a planet is given by:
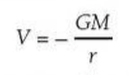
⇒ So the change in potential is:
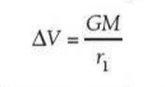
⇒ So the escape velocity for a planet can be calculated using:
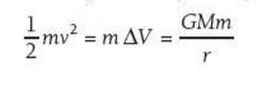

⇒ Since air molecules travel at approximately 500ms-1 on the surface of the Earth, they travel well below the Earth's escape velocity
Extra
⇒ Also see our notes on: