Newton's Law of Gravity
What you should know
⇒ The Earth, other planets and stars produce gravitational fields, which exert a force on other massive objects
⇒ A gravitational field exerts a 'non-contact' force, which acts over very long distances
⇒ Gravitational field strength, g, is defined as the force that acts on a mass of 1kg. On Earth, g = 9.81 Nkg-1
⇒ A planet's or stars gravitational field strength, at its surface, depends on its mass and radius
⇒ The gravitational potential energy, Ep (in J), gained by a mass, m (in kg), lifted through a height, h (in m), in a uniform gravitational field, g (in NKg), is given by E = mgh
⇒ The kinetic energy of an object is given by 1/2 m v2
Summary
⇒ Newton's law of gravitation states that the gravitational force of attraction between two point masses, m1 and m2 (measured in kg), separated by a distance, r (in metres), is given by:

⇒ This constant can only be accurately measured by careful laboratory experiment
⇒ Although Newton's law only applies to point masses, it can also be used to calculate the force of attraction between two large spherical objects (like planets and stars) because a sphere behaves as if all the mass were concentrated at the centre
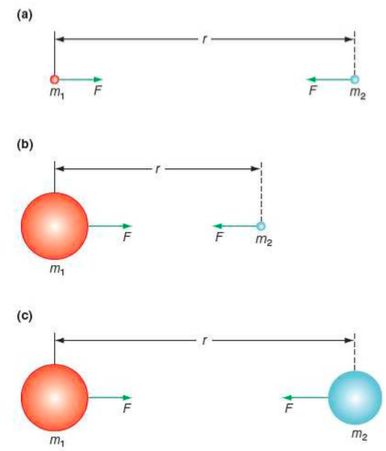
⇒ So Newton's law can be correctly used to calculate the force of attraction in each of the cases above:
- In (a), the force between two point masses
- In (b), the force between a planet and a small mass
- In (c), the force between two planets or stars
⇒ Newton's law cannot be used to calculate the force between two irregularly shaped objects, unless a complicated summation of the forces is made
Example


The Inverse Square Law
⇒ When Newton formulated his law of gravity, he imagined that the law of gravity spreads out in the same way as light spreads out from a candle
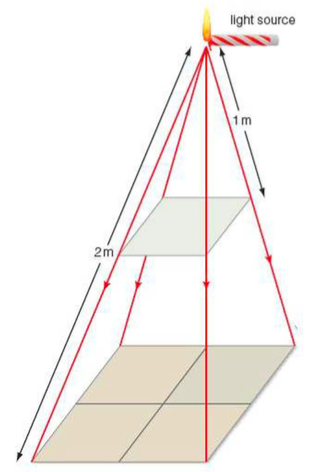
⇒ This image shows his idea
⇒ When you hold a card at a distance of 1m from the candle, you see a particular intensity of light, l
⇒ When you move a distance of 2m from the candle, the same amount of light now spreads out over four cards of the same area
- So the light intensity is now a quarter of its original value, 1/4 l
⇒ Light intensity obeys an inverse square law:
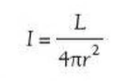
⇒ Here I is the intensity of light in W m-2, L is the luminosity of the light source (the amount of energy emitted per second) in W, and r is the distance away from the light source in m
⇒ The factor 4π comes into the equation because the light spreads out into a sphere, and the surface area of a sphere of radius r is 4πr2
Extra
⇒ Also see our notes on: