Conduction and Convection
Introduction
⇒ Houses need to keep heat in, so it is super important that there are ways to prevent heat from getting 'lost'
Conduction within solids
⇒ The reason why houses lose a lot of heat through their windows when shut is because of conduction: the heat moves from the warm interior to the cold exterior
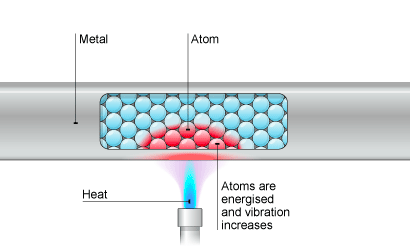
⇒ Solid materials have tightly packed particles, meaning that when one particle vibrates the particle next to it is bumped, causing that to vibrate too. This causes a chain of vibrating particles
⇒ When heat is applied to something, the particles in it move faster and they pass on their kinetic energy (i.e. the movement) to each neighbouring particle
⇒ This process continues untill the kinetic energy (or heat) is spread throughout the entire solid material
⇒ Metals are good conductors, whereas non-metals are good insulators
⇒ Liquids and gasses are also good insulators - the particles in liquids and solids aren't so close together, meaning heat moves slower through it
Convection in liquids and gasses
⇒ When heating up liquids and gasses, the particles contained within it begin to speed up and become less dense and rise
⇒ The warmer, and therefore less dense, liquid and gas will then rise above its cooler surroundings
⇒ Then the warmed liquid/gas will cool causing it to drop back towards the source that provided the heat, causing a continuous cycle known as a convection current
⇒ A radiators works by utlising convection to move heat around a room
⇒ Convection won't happen within a solid because the particles cannot move around
⇒ Convection can be reduced by stopping the movement of the liquid/gas particles. For eample, you can fill cavities (i.e. spaces) in between walls with various materials, which means convection is prevented
- Although this still allows for conduction, this transfer of heat will be very slow in comparison to convection