Melting and Boiling
Introduction
⇒ The reason why water can't get hotter than 100°C is because of something called latent heat
Breaking Intermolecular Bonds
⇒ Heating a liquid causes the particles it contains to move quicker through heat energy. When this energy is large enough, the particles overcome their attraction to each other causing bubbles of gas (in other words, the liquid is boiling)
⇒ When heating a solid, the particles it contains begin to vibrate faster until the forces between the particles are overcome and they begin to move (in other words, the solid is melting)
⇒ When something is melting or boiling, you are still giving that substance energy, but the energy is being used for breaking intermolecular bonds rather than raising the temperature of the substance
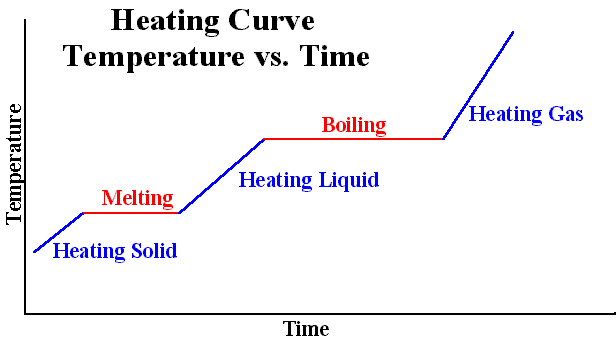
- So before a substance melts or boils, the heat energy given to that substance causes the particles to move and therefore change temperature. However, once the substance begins to melt/boil, the heat energy given to that substance no longer cuses the particles to move (so there is no change in temperature); instead, the energy given to it is used to breaking the intermolecular bonds within the substance (which, as a result, causes a substance to change from solid to liquid to gas)
- As an example, if you had some ice with a temperature of -10°C and you heat it up, the temperature of the ice will rise until it gets to 0°C, which is when the ice will start melting. When the ice is melting, the temperature of the ice will not change - thus the heat needed to make the ice cube completely melt is the latent heat
⇒ When you condense or freeze a substance, bonds are formed between the particles within the substance, which causes energy to be released. Therefore, energy does not decrease until the substance has transformed into a liquid (through condensing) or to a solid (through freezing)
Specific Latent Heat
⇒ The specific latent heat of melting = the total amount of energy that is required to melt 1 kilogram of something without changing its temperature
⇒ The specific latent heat of boiling = the total amount of energy that is required to boil 1 kilogram of something without changing its temperature
⇒ Obviously the specific latent heat will be different for different substances
⇒ Remember this formula:
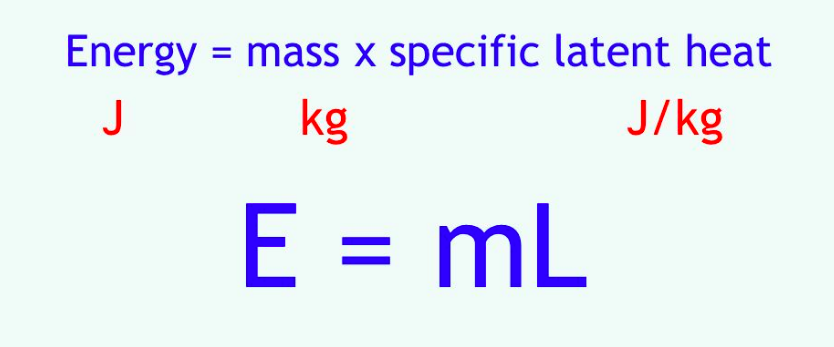
- So the formula tells us how much heat energy is needed to go into a material to change it from a solid to a melted liquid.
- If you apply heat to ice, it will melt. If you put a thermometer into the mixture you will see the temperature gradually rise, and then stop.
- The temperature remains the same for a while and then it rises again. The reason this happens is that a lot of energy is needed to break the bonds between the particles in the solid to change it to a liquid.
- When all the bonds are broken, the temperature rises again.
Example
⇒ The specific latent heat of water (for melting) is 334,000 J/kg. How much energy is needed to melt an ice cube with a mass of 7 grams at 0°C?
- Energy = 0.007 x 334,000J = 2338J
⇒ The specific latent heat of water (for boiling) is 2,260,000 J/kg, 2,825,000 J of energy is used to boil dry a pan of water at 100°C. What was the mass of the water in the pan at the beginning?
- Mass = Energy⁄SLH = 2,825,000⁄2,260,000 = 1.25kg