Detecting Nuclear Radiation
Introduction
⇒ Alpha, beta, and gamma radiation are all enegetic enough to pull electrons away from atoms
⇒ The atoms that have had electrons removed in this way are now charged particles, or ions, and hence the name ionising radiation.
The Cloud Chamber
⇒ One of the earliest ways of detecting ionising nuclear radiation was the Cloud Chamber
⇒ Clouds are artificially created by rapidly expanding air saturated with water in a sealed container
⇒ As ionising radiation passes through the cold damp air, tiny water droplets form around the ions produced
⇒ An alpha particle that passes through the chamber will, therefore, leave a thick and short track of droplets
⇒ A beta particle has thinner and slightly longer tracks (which can be straight or curved) because it is less ionising and smaller than the alpha particle, so loses its energy slower in the chamber
⇒ Gamma radiation is weakly ionising, so leaves no tracks at all
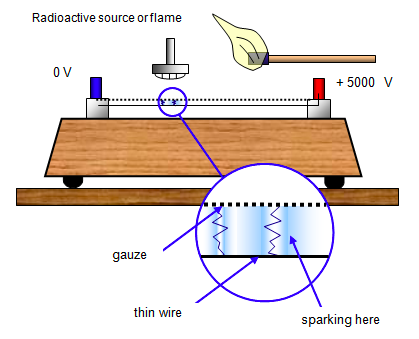
The Spark Counter
⇒ The Spark Counter only detects highly ionising alpha particles
⇒ It is made from a metal gauze placed about a millimetre away from a thin wire. A voltage is applied between the two so that sparking takes place between them - this usually requires some 4000 - 5000 volts. The voltage is then reduced until the sparking stops.
⇒ If an alpha-source is brought up close to the gauze it will ionise the air, and sparks will occur between the gauze and wire
⇒ With beta and gamma sources insufficient ions are usually produced for sparking to take place.
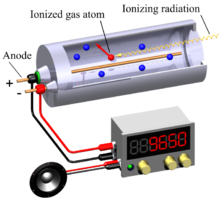
Geiger-Muller Counter
⇒ This is designed to detect and count the amount of radioactive emissions automatically
⇒ The ionising radiation (alpha, beta or gamma radiation) enters into the tube, causing the gas inside the detector (usually helium, neon or argon) to ionise
⇒ The ions (i.e. the charged particles) are attracted to the oppositely charged electrodes, causing a pulse of current, which is seen as a 'count' on the device
⇒ The big benefit of a geiger-muller counter is that they can detect all three types of radiation